In the era of Industry 4.0, the rapid advancement of technology has fundamentally transformed the way products are created. From error-prone hand-drawn sketches on paper, manufacturing enterprises have now transitioned to a fully digitized reference framework. This is the convergence of the four pillars: CAD CAM CAE PLM. These are not merely standalone software tools, but an integrated, closed-loop ecosystem that serves as the backbone of smart manufacturing.
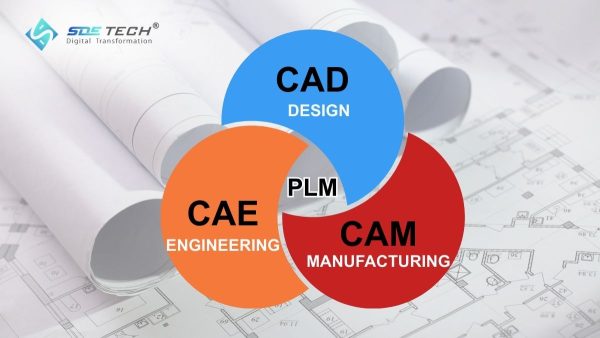
1. What are CAD, CAM, CAE, and PLM?
To fully understand how a modern factory operates, we need to break down each concept and examine the technical depth and practical role of CAD, CAM, CAE, and PLM.
1.1 What is CAD (Computer-Aided Design)?
CAD – Computer-Aided Design – refers to the use of computer technology to assist engineers in creating, modifying, analyzing, or optimizing an engineering design. CAD replaces manual drafting methods with highly accurate geometric models. There are two main types of CAD:
- 2D CAD: Focuses on flat technical drawings, electrical schematics, or detailed cross-sections.
- 3D CAD: Creates solid models (Solid Modeling) or surface models (Surface Modeling). This is the most critical foundation for visualizing products from all angles and for performing subsequent steps such as simulation or manufacturing.
CAD significantly increases design productivity compared to hand drafting, improves accuracy, and allows flexible storage and modification of drawings. Most importantly, CAD data is an indispensable input for CAM and CAE systems.
Modern trend: The emergence of Cloud CAD is removing hardware barriers. Engineers can collaborate on the same 3D model in real time, enabling design workflows that are no longer constrained by geographical location.
1.2 What is CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing)?
CAM – Computer-Aided Manufacturing – is the use of software to control machinery and related equipment in the manufacturing process. CAM serves as the direct bridge that transforms digital models into physical products.
How it works: CAM software takes geometric data from CAD models. Engineers then define tooling parameters, cutting speeds, and toolpaths. Finally, through a post-processor, the software generates G-code—the language that CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines can interpret and execute.
CAM eliminates manual operation errors, optimizes material usage, and reduces machining cycle time. Today’s advanced CAM systems can also program complex multi-axis machines (4-axis, 5-axis), tasks that are nearly impossible with manual programming.
1.3 What is CAE (Computer-Aided Engineering)?
CAE – Computer-Aided Engineering – involves using simulation algorithms to evaluate product performance. If CAD is about shaping the design, CAE is about “stress-testing” that design in a virtual environment before it is manufactured.
Common analysis methods include:
- FEA (Finite Element Analysis): Evaluates stress, strength, and deformation of components under mechanical or thermal loads.
- CFD (Computational Fluid Dynamics): Simulates fluid or gas flow, critical in the design of engines, cooling systems, and vehicle aerodynamics.
- MBD (Multi-Body Dynamics): Analyzes the motion of mechanisms consisting of multiple interacting components.
CAE helps dramatically reduce the number of physical prototypes. Instead of building and testing real parts until failure, companies can run thousands of virtual tests to identify the optimal solution—saving substantial costs and significantly shortening R&D cycles.
1.4 What is PLM (Product Lifecycle Management)?
PLM – Product Lifecycle Management – is not a tool for creating geometry or machine code, but a data management strategy. PLM manages the entire journey of a product, from initial concept and design, through engineering and manufacturing, to market release, maintenance, and eventual disposal.
Core functions include:
- Design data management (PDM).
- Bill of Materials (BOM) management.
- Change management and workflow control.
- Connecting departments (Engineering, Manufacturing, Purchasing, Sales) on a single data platform.
PLM acts as the “Single Source of Truth.” In large-scale projects involving thousands of components, PLM ensures that every engineer is working with the latest, up-to-date design version, eliminating manufacturing errors caused by the use of outdated or incorrect data.

2. The Differences and Relationship Between CAD, CAM, CAE, and PLM
Although their names are similar, their roles within the value chain are fundamentally different. However, they do not operate independently; instead, they form a continuous and connected data flow.
| Criteria | CAD | CAE | CAM | PLM |
| Role | Creation: Building the product geometry. | Validation: Analyzing and optimizing performance. | Execution: Generating machine control instructions for manufacturing. | Governance: Coordinating all data and processes. |
| Output | 3D models, technical drawings. | Analysis reports, optimized parameters. | G-code, machining programs. | Product structure, change history. |
| Stage | Early phase (R&D). | Middle phase (Engineering design). | Final phase (Manufacturing). | Throughout the entire lifecycle. |
A product typically begins in CAD, where the initial design is created. The model is then transferred to CAE to analyze strength and performance. If issues are detected, the data loops back to CAD for revision. Once the design is validated, it moves to CAM for manufacturing programming. All of these steps are continuously recorded, controlled, and synchronized within the PLM system.
3. Leading CAD/CAM/CAE/PLM Software Solutions Today
The market offers many solutions from major technology providers that enable enterprises to implement this digital workflow. Below are some representative and reputable names:
3.1 CAD Design Solutions
CrownCAD: A standout example of next-generation design. Operating entirely on a web-based platform, CrownCAD enables companies to streamline hardware investments while still delivering powerful 3D design capabilities and excellent real-time team collaboration.
ProgeCAD: A professional 2D/3D CAD software similar to AutoCAD, using the standard DWG format. It comes with an integrated library of over 22,000 industry-specific symbols. With strong PDF-to-DWG conversion capabilities and a perpetual license model, ProgeCAD is a highly cost-effective solution for technical drafting and design.

3.2 Specialized Simulation (CAE) Solutions
Cadmould Flex: A dedicated solution for the plastic injection molding industry, enabling simulation of polymer melt flow into the mold to predict defects such as warpage, air traps, and voids.
Particleworks: A CFD solution based on particle methods. This breakthrough technology enables the analysis of highly complex fluid interactions that are difficult or impossible to handle accurately with traditional mesh-based approaches.
3.3 Machining & Optimization (CAM) Solutions
Mastercam: The world’s most widely used CAD/CAM software, acting as a “bridge” that converts 2D/3D designs into G-code to control CNC machines (milling, turning, wire EDM, etc.). Its outstanding strength lies in Dynamic Motion technology, which optimizes toolpaths to achieve up to 75% faster machining while significantly extending cutting tool life.
TopSolid: An integrated CAD/CAM/ERP solution, renowned for its intelligent manufacturing data management. The key differentiator of TopSolid is its full associativity: when a design (CAD) is modified, toolpaths (CAM) and technical drawings are automatically updated instantly, ensuring consistency across the entire workflow.
In addition, several complementary CAM solutions support machining optimization, including:
- VoluMill: More than a conventional CAM tool, VoluMill is a high-efficiency toolpath optimization solution. It maintains a constant tool load, enabling deeper and faster cuts, extending tool life, and reducing machining time by up to 70%.
- MANUSsim: A CNC machine simulation solution that verifies machining safety and detects potential collisions between tools, fixtures, and machine components before actual production, effectively protecting valuable manufacturing assets.
3.4 Leading Integrated Solutions (Siemens Digital Industries Software)
Siemens is a global leader in delivering a fully integrated digital manufacturing portfolio, including:
- NX: A high-end CAD/CAM/CAE platform, widely adopted by major aerospace and automotive corporations.
- Solid Edge: A powerful 3D design solution tailored for small and medium-sized enterprises.
- Teamcenter: The world’s most widely used PLM software, managing all product and manufacturing data across the lifecycle.
In Vietnam, these trusted solutions are consulted and implemented by SDE Tech – a reliable partner helping manufacturers select and deploy the most suitable software configuration aligned with their specific production requirements.

4. Frequently Asked Questions
4.1 Is PLM necessary for small and medium-sized enterprises?
Many small businesses believe that PLM is only suitable for large corporations. However, once your company starts managing multiple projects, multiple design versions, and faces difficulties in document control, PLM (or PDM modules) becomes essential to avoid costly production errors.
4.2 Is Cloud CAD as secure as traditional installed software?
Solutions such as CrownCAD leverage the security infrastructure of leading cloud service providers like AWS and Azure. Data is encrypted and continuously backed up, minimizing the risk of data loss caused by hard drive failures or malware on local computers. In practice, Cloud CAD solutions often offer higher security than poorly maintained personal workstations.
4.3 How can I choose the right CAE software?
You first need to clearly define your engineering challenges. For plastic injection molding applications, Cadmould Flex is the top choice. For complex fluid flow analysis, Particleworks is more suitable. Consulting with experts from solution providers such as SDE Tech helps businesses avoid incorrect or inefficient software investments.
The convergence of CAD, CAM, CAE, and PLM is the key enabler for manufacturing enterprises to transition from traditional machining to smart manufacturing. A clear understanding of each system and the right selection of proven software solutions (such as NX, CrownCAD, VoluMill, etc.) not only boosts productivity but also strengthens a company’s position within the global supply chain. If your organization is beginning its digital transformation journey, the first step should be standardizing design and manufacturing data today.
- Website: sde.vn
- Email: sales@sde.vn
- Hotline/Zalo: 085 256 2615 – 0909 107 719
Leave your information to receive fast consultation.:

 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt 日本語
日本語 한국어
한국어



